
Balancing Act: Benefits and Challenges of Robotic Process Automation in Corporate Finance
In the era of digital transformation, organizations in various industries are seeking new solutions and innovations to improve their business processes, ensure operational efficiency, and enhance their competitive advantage. Recently, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Corporate Finance has emerged as a powerful technology to revolutionize the way companies operate. RPA is the umbrella of all technologies that uses intelligent automation to perform repetitive office tasks of human workers. By automating these repetitive tasks, RPA offers the potential to unleash new standards of productivity, compliance, cost reduction and workforce happiness. In addition to these benefits, RPA can also streamline complex financial processes (such as invoice processing and reconciliation) and improve the decision process through data analytics, contributing to enhanced financial forecasting and planning. Furthermore, its scalability and adaptability make it valuable for organizations aiming to stay competitive in the corporate finance landscape.
The existing research unambiguously confirms the positive effects of RPA on organizations: Kaya (2019) concluded that financial RPA will significantly improve error-free and accurate transactions while increasing the efficiency in financial monitoring and auditing. Lamberton (2017) implied that RPA in finance can lead to significant cost reduction (50% or more) and “typically provides return on investment in less than a year”. Moreover, a global report by Deloitte in 2018 indicated that 80% of companies experienced improvement in employee satisfaction and 93% of organizations reported improved compliance through the adoption of RPA.
While RPA provides vast potential to unleash new standards of productivity and efficiency, it also poses several challenges in implementation and utilization. According to the Deloitte Global Robotics Survey (2018), one significant challenge is the complexity of financial processes and involve complex workflows, extensive data handling, and compliance requirements. Additionally, lack of IT readiness will hinder further scaling and low ambition among top executives pose additional obstacles to successfully implement RPA. The survey suggests that in 2018, only 4% of the respondents have reached substantial scale regarding RPA and that 32% have not yet started their RPA journey. These figures indicate that organizations are facing considerable difficulties to unlock full RPA potentials.
In this paper, we will look at several scientific articles and reports on financial RPA and pull all the existing information to give readers a clear and complete picture of this field. We’ll be focusing on key topics like how RPA helps improve efficiency, cuts down costs, and comply with rules easier.
This paper combines a wide range of information in one place and while there exists lots of studies, many only focusing on one or two aspects of financial RPA. The paper is designed to provide a holistic view of the main benefits and challenges coming with RPA, simplifying the big picture. This work will be a useful resource for professionals, decision-makers, and researchers to support them making better decisions and plans when it comes to using RPA in the finance world.
The benefits of RPA in Corporate Finance
Introduction into RPA
Moving on to the theoretical background of RPA, it is essential to acknowledge its transformative potential in automating repetitive, rule-based tasks. As already mentioned, RPA leverages software robots to perform these tasks with speed, accuracy, and reliability, thus freeing up valuable human resources to focus on more strategic and analytical activities. According to Boulton (2018), these bots are capable of imitating human interactions with software systems, data manipulation, and executing predefined rules and can be trained to perform a wide range of tasks, such as data entry & reconciliation, report generation, invoice processing, and compliance checks, among others. They can handle high transaction volumes without significant additional resources and can adapt to evolving regulatory requirements (Gartner report, 2021).
Applications of RPA in Finance
- Transaction Processing: RPA can automate various transactional processes in finance, including accounts payable and receivable, order processing, and reconciliation. By extracting data from different sources, validating it, and entering it into financial systems, RPA enables faster and more accurate transaction (Kaya, 2019).
- Reporting and Compliance: RPA can streamline the generation of financial reports by automating data extraction from multiple systems, performing calculations, and generating customized reports (KPMG, 2018).
- Financial Analysis: RPA can support financial analysis by automating data collection, data cleansing, and data transformation processes. It can extract relevant financial data from various sources, perform calculations, and generate insights for decision-making purposes (Kaya, 2019).
- Risk Management: RPA can be employed to automate risk management processes in finance. By monitoring and analyzing data from different systems in real-time, RPA bots can identify potential risks, trigger alerts, and support risk mitigation strategies (Lamberton, 2017)
Literature review
In recent years, digital transformation has become one of the hottest topics within organizations as it helps to leverage technology and digital solutions to enhance and streamline various aspects of financial operations, processes, and services. Meanwhile, RPA is an important aspect of digital transformation and helps the organization to focus more on the business rather than on repetitive tasks. People will spend less time on preparing reports and more time on analyzing important business insights from real-time data empowering them to make better strategic decisions. A Deloitte survey from 2018 predicts that “new service delivery models will emerge as robots and algorithms join a more diverse finance workforce” in the coming years and according to the study, corporations have 3 top priorities:
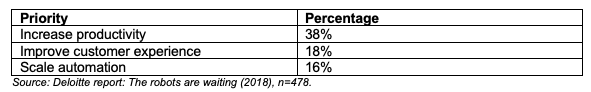
At the same time, Deloitte also concluded that more than 90% of companies who have implemented RPA believe that RPA has met or even exceeded their expectations regarding major criteria:

Source: Screenshot from Deloitte report: The robots are waiting (2018), n=81.
The data presented from the Deloitte report underscores the important role that RPA and digital transformation play in improving operational efficiency and enhancing customer experiences. With over a third of corporations prioritizing increased productivity, RPA is a critical tool, removing the burden of repetitive tasks and promoting an environment where human resources are directed towards more strategic, insight-driven roles.
Another report by KPMG (2021) delves deeper into RPA particularly for the corporate finance area. KPMG provides some recommendations on how to correctly identify processes for RPA:
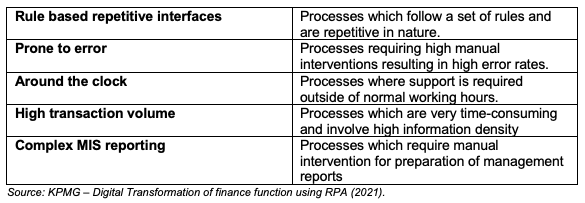
Based on these recommendations, the report summarizes 7 main areas where RPA could significantly benefit the business:
- Payroll processing: Automation of the entire process leads to fewer errors and faster turnaround time.
- Invoice validation, processing, and payment: Automation leads to minimized human input.
- Refund processing: Automation leads to increased customer satisfaction and firm reputation.
- Price comparison: RPA leads to cost optimization.
- Compliance: RPA leads to less errors and increase compliance.
- Financial planning: Automation decreases repetitive tasks and empower better decision-making.
- Investment guidance: Automation of investment advisory will reduce the cost of human advisors and increase customer involvement in the market.
Concluding from the above benefits, RPA can therefore lead to:
- Increased operational visibility.
- Stronger data security.
- Reduction in cost.
- Improved compliance.
- Optimized efficiency and better service.
Both Deloitte and KPMG reports accentuate the central role that Robotic Process Automation (RPA) plays in the broader landscape of digital transformation, especially within the financial operations and services sectors. There are many similarities in the findings of these two influential studies, underscoring a consensus on the benefits that RPA delivers in for businesses globally. One of the findings echoed in both reports is the enhancement in operational efficiency and productivity facilitated by RPA. Deloitte highlights that a significant portion of corporations (38%) prioritizes the increase of productivity. This aligns with KPMG’s identification of RPA’s capability to streamline complex and high-volume transaction processes, such as payroll and invoice processing, resulting in improved operations and reduced errors. Moreover, Deloitte’s survey shows that 18% of corporations are prioritizing improving the customer experience. This is paralleled in KPMG’s findings, where the implementation of RPA in areas like refund processing not only enhances the process but significantly improves customer satisfaction, bolstering the organization’s reputation. The enhancement in compliance and data security is another mutual highlight. KPMG specifically notes the role of RPA in reducing errors and enhancing compliance, a result identified in Deloitte’s finding where over 90% of companies acknowledged that RPA met or exceeded their expectations in these critical areas. In conclusion, both Deloitte and KPMG offer a harmonized view on the important profound impacts of RPA in the area of digital transformation.
We get similar results when comparing the findings of the two reports with those of scientific papers. Kaya (2019) identified below benefits when it comes to RPA for corporate finance:

After the analysis provided by Kaya, we will unveil a model that summarizes the comprehensive scope of RPA benefits based on the literature review. This model is designed to offer a holistic view of the impacts of RPA, presenting the interplay between diverse benefits that elevate organizational performance, customer experience, and strategic insight.
The Five-Dimensional model of RPA benefits
Below is a holistic model that categorizes the benefits of RPA into five core dimensions, integrating insights from the Deloitte, KPMG, and Kaya (2019) reports. This model is designed to offer readers a comprehensive view of the diverse advantages that RPA delivers to organizations, particularly within the context of financial operations and services.
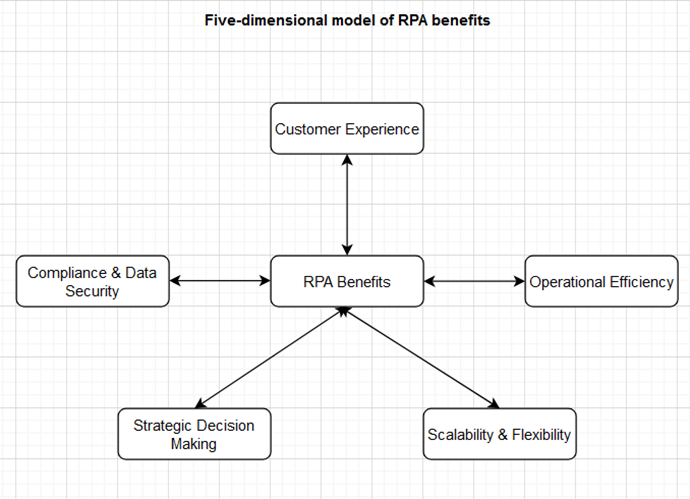
Source: Own diagram.
Operational Efficiency
- Increased Productivity: Automation of repetitive, rule-based tasks enables staff to focus on more value-added activities.
- Cost Reduction: RPA reduces operational costs, as robots are cost-effective and can work 24/7.
- Performance Improvement: Enhanced speed and accuracy in task execution lead to performance boost.
Customer Experience
- Enhanced Satisfaction: Faster and error-free services improve customer satisfaction.
- Streamlined Processes: Automated processes ensure timely and efficient service delivery.
- Personalization: Data analytics coupled with RPA enables tailored service offerings.
Compliance & Data Security
- Error Reduction: Automation reduces the risk of human errors, enhancing data accuracy.
- Enhanced Compliance: Automation ensures adherence to regulatory requirements and standards.
- Data Security: RPA ensures data handling and processing according to security protocols.
Strategic Decision Making
- Advanced Analytics: Automation facilitates efficient data gathering and real-time analytics.
- Insight-Driven: Empowers organizations with actionable insights for informed decision-making.
- Resource Allocation: Redirects human resources to strategic, analytical, and creative tasks.
Scalability & Flexibility
- Adaptability: RPA allows easy scaling and adaptability to changing business environments.
- Technology Integration: Seamlessly integrates with existing systems and emerging technologies.
- Agile Operations: Enhances organizational agility through flexible and scalable automated processes.
In essence, this model captures the transformative impact of RPA, positioning it as an indispensable asset for organizations. It offers a holistic view of RPA’s multidimensional benefits that are instrumental in navigating the complexities of modern finance.
The challenges of RPA in Corporate Finance
Literature review
As with any innovative technology, the implementation of RPA in corporate finance is not without its challenges. These hurdles range from integration issues with existing systems to the need for significant initial investment, and from data security concerns to the management of change within the organizational structure and culture. This section aims to provide an insightful overview of the diverse challenges encountered in the integration of RPA in corporate finance. Through a comprehensive exploration, we aim to identify main problem areas to encourage new solutions to tackle these issues.
The Deloitte report (2018) found out that most companies in 2018 are still in the beginner’s phase in terms of RPA implementation:
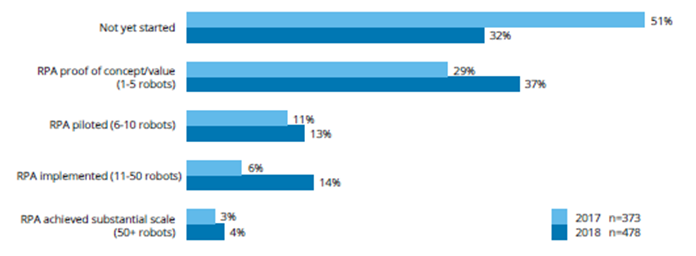
Source: Screenshot from Deloitte report: The robots are waiting (2018), n=81.
Armed with that information, the report identifies the biggest barrier of implementing RPA as follows:
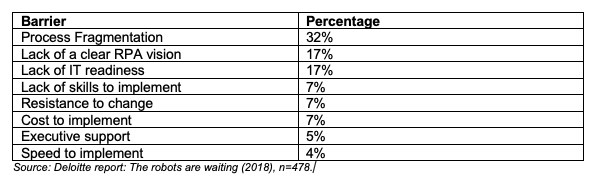
Process Fragmentation (32%):
Process fragmentation is identified as the most significant barrier, with 32% of respondents highlighting it. This issue is related to the complexity and fragmentation of existing processes within corporate finance departments. The fragmented nature of these processes makes it challenging to seamlessly integrate RPA solutions, as these automated systems require streamlined and well-defined workflows to operate effectively. Companies face difficulties in mapping out and optimizing their existing processes to create an environment where RPA can deliver the expected efficiency and cost-saving benefits.
Lack of a Clear RPA Vision (17%):
The second most cited barrier, at 17%, is the lack of a clear RPA vision. Organizations are struggling to develop and articulate a comprehensive strategy for the integration of RPA into their operations. A well-defined vision is essential to align all stakeholders, including management, employees, and investors, ensuring everyone is moving towards a common goal. The absence of a clear vision can lead to misaligned efforts, inefficient use of resources, and failure to achieve the desired outcomes from the RPA implementation.
Lack of IT Readiness (17%):
Equally ranking as the second barrier is the lack of IT readiness, also at 17%. This hurdle refers to the technical inadequacies and unpreparedness of the organization’s IT infrastructure to support and sustain RPA technologies. Adequate IT systems, support, and infrastructure are pivotal for the successful deployment and operation of RPA. Companies face challenges in updating and upgrading their IT systems to be compatible with RPA technologies, ensuring security, scalability, and performance to meet the operational demands and achieve ROI.
Next to the Deloitte report, in 2016, a report from Ernst and Young identified major issues which could lead to RPA implementation failure:
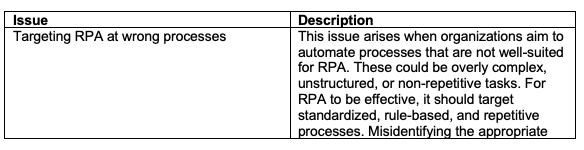

Source: Ernst & Young – Get ready for the robots (2016).
Ernst & Young’s report underscores the need for strategic RPA implementation. Key takeaways include targeting suitable, rule-based tasks, employing a tailored delivery strategy, and ensuring technical readiness. Organizations should avoid over-automation and ensure IT infrastructure support. RPA isn’t a standalone solution; it should integrate with broader organizational and process optimization strategies to maximize ROI effectively.
Strategic model of RPA Challenges
By combining the results of both Deloitte and Ernst & Young reports, we can come up with a holistic view on the challenges implementing RPA in finance (Strategic model of RPA Challenges):
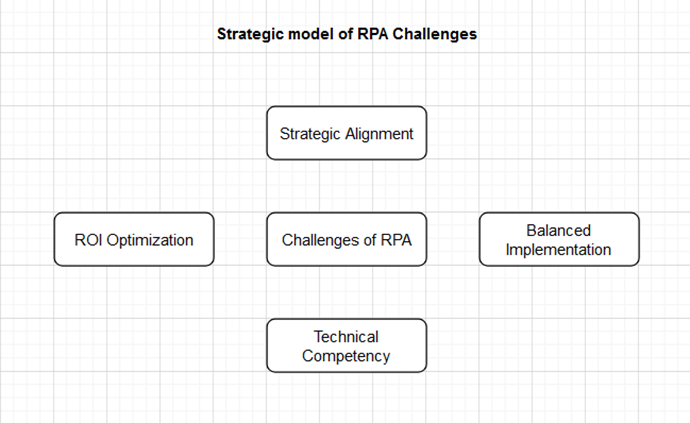
Source: Own diagram.
Strategic Alignment:
- Ensure RPA targets are rule-based, repetitive, and standardized processes.
- Develop a clear, comprehensive, and aligned RPA vision and strategy.
Technical Competency:
- Enhance IT infrastructure readiness to support RPA integration and operation.
- Build/acquire technical skills for effective POC development and RPA implementation.
Balanced Implementation:
- Employ a tailored and well-executed delivery methodology.
- Avoid over-automation; focus on tasks optimal for RPA and consider human-machine collaboration.
ROI Optimization:
- Consider RPA as part of a broader strategy, including process optimization, change management, and continuous improvement, to maximize financial and operational benefits.
By addressing these integrated challenges with targeted strategies, organizations can navigate the complexities of RPA implementation, optimizing both the process and outcomes for enhanced efficiency, cost savings, and ROI.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is highly influential in the evolution of corporate finance, serving as a driver for enhanced efficiency, cost reduction, and strategic optimization. The comprehensive exploration of existing literature and reports, as illustrated in this paper, unveils opportunities and challenges during the journey of RPA integration in corporate finance.
Realizing the Benefits
Insights from prominent reports and academic research underscores RPA’s high impact in automating repetitive, rule-based tasks. Our Five-Dimensional model of RPA benefits reveals advantages spanning operational efficiency, customer experience enhancement, compliance and data security fortification, strategic decision-making empowerment, and scalability and flexibility augmentation.
Navigating the Challenges
Benefits are always connected with challenges. The Deloitte and Ernst & Young reports illuminate these hurdles, ranging from process fragmentation and lack of clear RPA vision to technical and IT readiness deficits. Our strategic model of RPA challenges explains these complexities.
The Road Ahead
The path forward for corporate finance professionals, decision-makers, and researchers is connected by a need for balanced, strategic, and reasonable approaches. RPA is a strategic tool—its optimal utilization lies in the alignment of technology, strategy, and human capital.
Organizations are called upon to combine the technical capabilities of RPA with the human ingenuity. A harmonious integration of these elements can lead to unprecedented innovation, efficiency, and strategic transformation. The investment in RPA should be complemented equally by enhancing IT infrastructure, developing workforce competencies, and fostering an organizational culture that is agile, adaptive, and receptive to change.
Bibliography:
Kaya, C., & Turkyilmaz, M., & Birol, B., (2019). Impact of RPA Technologies on Accounting Systems. Muhasebe ve Finansman Dergisi, Nisan/2019, 235-250.
Lamberton, C., & Brigo, D., & Hoy, D., (2017). Impact of Robotics, RPA and AI on the Insurance Industry: Challenges and Opportunities. The Journal of Financial Perspectives: Insurance, 8-20.
Boulton, C., (2018). What is RPA? A revolution in business process automation. Computerworld Hong Kong, May/2018.
Gartner., (2021). The Digital Future of Finance. Gartner for Finance.
Gartner., (2019). White Paper – Revolutionizing via Robotics: Hear from a Peer.
Deloitte., (2018). The robots are waiting – Are you ready to reap the benefits?
KPMG., (2021). Digital Transformation of finance function using RPA.
Author: Mingzhe Li, student LIGS University
Approved by & Co-author: Prof. Grigory Sergeenko, lecturer LIGS University



