Effect LinkedIn Automation: An Analysis of LinkedIn Marketing Automation with use of low- and no-code tools
Author: Alderd J. Froolik, LIGS University, Honolulu, Hawaï, USA
Supervisor: Dr. Roberto A. Llauro, Adjunct Professor of LIGS University
Author Note
Alderd J. Froolik https://orcid.org/0009-0009-1736-7232
Correspondence concerning this article should be addressed to Alderd J. Froolik, LIGS University, p/a Zwanebloem 47, 2408LT Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands. Email: alderd@me.com
Author Biography
Alderd J. Froolik received a Master of Business Administration (MBA) and a Master Of Science (MSc.) both with a major in marketing from EDU Effective in 2023 and graduated summa cum laude (97%) on both masters. He is currently a Doctor of Business Administration (DBA) candidate at Quest Sales & Marketing Automations, under the supervision of LIGS University. His research areas include marketing automations, AI technologies, and low- and no-code tools.
Abstract
This research study delves into the critical examination of automation’s effectiveness on LinkedIn, a leading B2B platform that facilitates professional connections for business and employment purposes. Given the rapid pace of today’s business environment, professionals face the challenge of dedicating sufficient time to actively engage on LinkedIn to leverage its full potential. With projections indicating a user base expansion to 1 billion, including over 300 million active users and access to 57 million businesses (Robert C. Stern “LinkedIn Stats Looking Into 2023”), active participation on LinkedIn is increasingly becoming a necessity. The study highlights the importance of maintaining an active profile through regular content posting, as businesses posting twice weekly experience a twofold increase in engagement, and those posting 20 times monthly significantly extend their reach within their target market. Additionally, the research underscores the benefits of completing and continually updating LinkedIn profiles, which can result in 40 times more opportunities, and reveals that crafting long-form content, incorporating multiple images and headlines, significantly enhances engagement rates. With the daunting task of staying active and relevant on the platform, this study aims to explore the impact of various automation tools designed to streamline the process of efficiently managing content creation and publication on both personal and business LinkedIn pages.
“Effect LinkedIn Automation”: An Analysis of LinkedIn Marketing Automation with use of low- and no-code tools
“Time is money” – Benjamin Franklin once said. To get the most out of LinkedIn you must invest loads of time. “The key is in not spending time, but in investing it.” – Stephen R. Covey, author of the Time Management Matrix. Automations combined with AI can save hours a week. This research will show why investing in automations is preferred over investing in time. The automations are created on the Integration platform as a service (iPaaS) Make.com, formerly known as Integromat. The app used in the automations to (re)write content is ChatGPT.
ChatGPT (Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer) is a chatbot developed by OpenAI and launched on November 30, 2022. Based on a large language model, it enables users to refine and steer a conversation towards a desired length, format, style, level of detail, and language. With the introduction of the GPT4 model it is extremely capable to be pre-trained in writing styles and generate high quality content in large volumes in that pre-trained style. The data for generating the content can be retrieved from a website, a database, a catalog, an RSS feed, or basically any given source. The order to generate the required content, named a prompt, will follow the guidelines from the trained or in a general manner. This content can be posted on LinkedIn personal profiles or on a business page using the same iPaaS platform. Posts can be scheduled on any give time or interval to the maximum by LinkedIn allowed number of daily posts which is about every 3 hours interval.
To write a blogpost of 2500 characters will take about 1 hour for a simple article and up to several hours for more in-depth articles. GPT4 embedded in an automation doesn’t take no more than the time to read the generated article which is about 8 minutes for this number of characters. This is purely on the initiation of the automation because when the thrust is in the competence of GPT4 of writing blogpost reviewing the content will not be required anymore.
Hypotheses
Content written to add value for each reader is important to fully utilize the power of LinkedIn. The content can be placed within LinkedIn on a personal account, on a business account, on a group, or on a business account. The hypotheses are that when content is posted on a consistent basis the number of visits and the number of followers will grow and the content will reach more readers. When an Integrated Platform as a Service (iPaaS) is used to automate the content production not only many hours will be saved but will contribute to the growth of the used channel within LinkedIn. Findings indicate that followers and website visits positively affect the amount of sales revenue, and sales posts and website visits drive the number of followers. In addition, social posts, new followers, and sales revenue positively influence engagement (Roberto Mora Cortez, et al. 2023).
Integrated Platform as a Service (iPaaS)
With iPaaS data streams are visible through apps connected to each other. Make.com (formerly known as Integromat) or Zapier are the most used iPaaS platforms. For this study the iPaaS Make.com was used and several selected, predefined apps to automatically create content and distributing this content on the personal and the business accounts on LinkedIn. Further engagement tools are used to collect the comments on the content and to provide a like on the given comments. The data flow structure, called scenarios, are developed to create content. Utilizing Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer (ChatGPT) technology in scenarios create tailored content with simultaneously monitoring incoming comments and reflecting on those comments automatically. All at scale.
Methodology
The study analyzes two datasets: the first encompasses a range of personal LinkedIn pages, focusing on the correlation between posting frequency and connection or follower growth; the second dataset examines a range of corporate pages, detailing regular posts, follower growth, and page views over several months. The analysis involves calculating Pearson correlation coefficients to assess the relationship between posting frequency and the respective engagement metrics.
The automation was built (Image 1) for each personal and business LinkedIn account using iPaaS Make.com (formerly Integromat) using blogpost either from a database or directly from Shopify, the text was parsed into plain text, the image was uploaded and ChatGPT is used to re-write the text to avoid duplicated content. Then it was all placed on LinkedIn. The interval varied for one a day to once a week.
Image 1. Make.com automation for retrieving data from Shopify, re-write the text and post on LinkedIn. Image screenshot taken from Make.com, scenario design and copyrighted by Alderd J. Froolik, MBA, MSc.
Results
Personal Pages
Analysis of the first dataset revealed a moderate positive correlation (r=0.503) between posting frequency and connection growth on personal LinkedIn pages. This suggests that individuals who post more frequently are likely to see a significant increase in their connections.
Corporate Pages
For corporate pages, particularly exemplified by the second dataset, we observed a very slight positive correlation (r=0.087) between posting frequency and new followers gained weekly. Additionally, a strong positive correlation (r=0.741) was noted between posting frequency and page views, indicating that increased posting significantly enhances page visibility.
Discussion
The findings illustrate the nuanced impact of posting frequency on LinkedIn engagement metrics. While both personal and corporate pages benefit from increased posting, the degree of impact varies. For personal pages, frequent posting is more directly associated with connection growth, emphasizing the value of consistent personal engagement. For corporate pages, although the effect on follower growth is minimal, the substantial increase in page views suggests that content visibility and brand awareness are significantly influenced by posting frequency.
These disparities underscore the importance of tailored content marketing strategies for personal versus corporate pages on LinkedIn. The findings also highlight the potential for strategic posting to enhance professional networking and brand visibility in a digital context.
Further research
To implement marketing automation on the LinkedIn platform at full scale; like automation of the comment reactions contributes significantly to the effect. When the LinkedIn API is connected to ChatGPT a reaction on a comment can be downloaded and a reaction can be created and, if the commenter is not already a connection, an invitation to connect can be send fully automatically using the same LinkedIn API. Also finding new connections through the LinkedIn API will contribute to growing the number of connections. The iPaaS Make.com can be used to set up API automations for LinkedIn and, if applicable divert connection data to a CRM to conduct further marketing like email marketing. However, LinkedIn maximizes the number of connections to 30.000. Above that number, an account can be followed only. Further research about the full utilization of the LinkedIn API should result in an enormous boost in engagement and growth in the number of connections of the targeted audience.
Conclusion
This research embarked on an explorative journey into the realms of LinkedIn marketing automation, harnessing the capabilities of low- and no-code tools on an iPaaS such as Make.com (formerly Integromat). By automating the posting process, the study uncovered a significant efficiency gain, saving approximately one hour per post, thereby illustrating the tangible benefits of integrating automation technologies into social media marketing strategies.
The analysis of the data revealed a nuanced understanding of the impact of automated posting on LinkedIn engagement metrics across personal and corporate pages. For personal pages, a moderate positive correlation was observed between posting frequency and connection growth, suggesting that automation facilitates not only efficiency but also effects personal brand building. Similarly, for corporate pages, the automation of posting activities demonstrated a significant positive effect on increasing page views, and a slight positive impact on follower growth.
Beyond the immediate efficiencies and the quantifiable impact on engagement metrics, the study ventured into the potential of full-scale automation through the LinkedIn API. Envisioned future research avenues include automating interactions such as replying to comments using ChatGPT integration, thereby enhancing engagement through timely and contextually relevant responses, and streamlining the process of sending out connection requests to expand professional networks efficiently at scale.
The potential of leveraging Make.com at scale to integrate deeply with the LinkedIn API presents a forward-looking perspective on how automation can transcend simple posting and engagement activities. This approach could redefine engagement strategies by providing personalized, AI-driven interactions that can significantly enhance the quality of engagement and foster a more interactive, responsive presence on LinkedIn.
In totality, the “Effect of LinkedIn Automation: An Analysis of LinkedIn Marketing Automation with Use of Low- and No-Code Tools” underscores the transformative power of automation in streamlining marketing workflows, enhancing engagement, and optimizing the strategic use of LinkedIn in B2B markets. By effectively integrating low- and no-code tools, marketers can unlock new efficiencies, drive higher engagement, and forge deeper connections with their audience, all while navigating the evolving landscape of digital marketing with agility and insight.
Looking into the future, the integration of automation technologies and AI-driven tools like ChatGPT within LinkedIn marketing strategies holds the promise of revolutionizing the way brands and individuals connect, engage, and grow their presence on this professional networking platform. The journey towards fully automated, highly personalized, and strategically optimized LinkedIn marketing practices is just beginning, and the potential for innovation and impact will change the way of conducting business in B2B markets.
Figures
Figure 1: Correlation between Posting Frequency and Connection Growth on Personal Pages
(Graph showing a moderate positive correlation with a trend line)
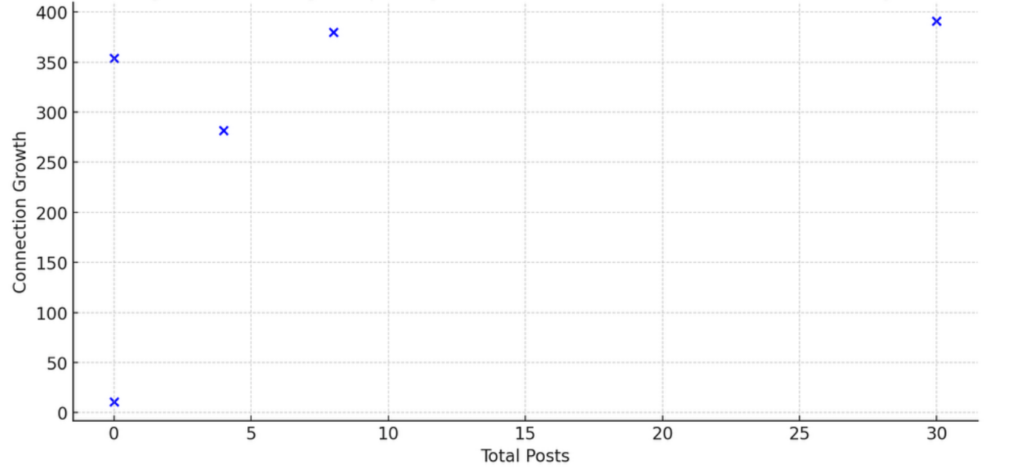
Figure 1 illustrates the moderate positive correlation between posting frequency and connection growth on personal LinkedIn pages. This graph shows that individuals who post more frequently tend to experience a significant increase in their connections.
Figure 2: Correlation between Posting Frequency and Follower Growth on Corporate Pages
(Graph showing a slight positive correlation with a trend line)
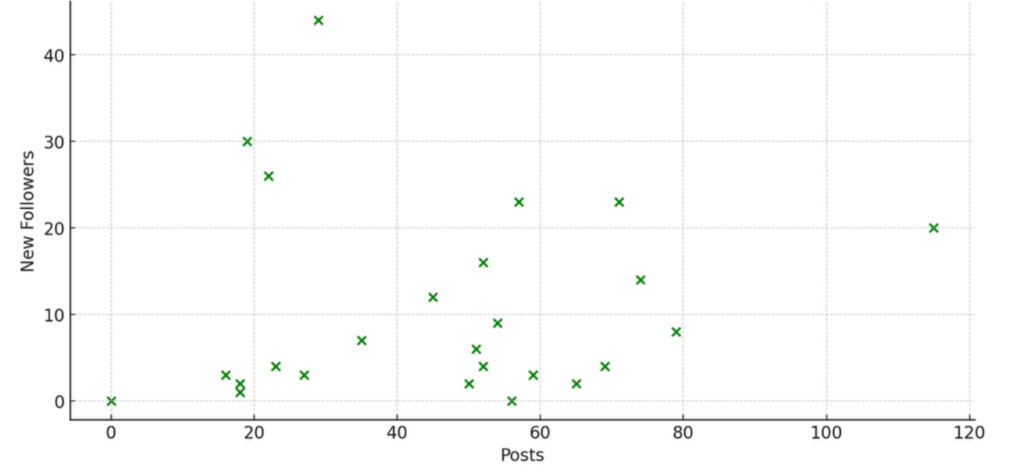
Figure 2 displays the very slight positive correlation between posting frequency and new follower growth on corporate pages, specifically analyzed through the PeponiXL dataset. Despite the minimal impact, there’s a marginal positive relationship indicating that posting more can slightly increase the number of new followers gained.
Figure 3: Correlation between Posting Frequency and Page Views on Corporate Pages
(Graph showing a strong positive correlation with a trend line)
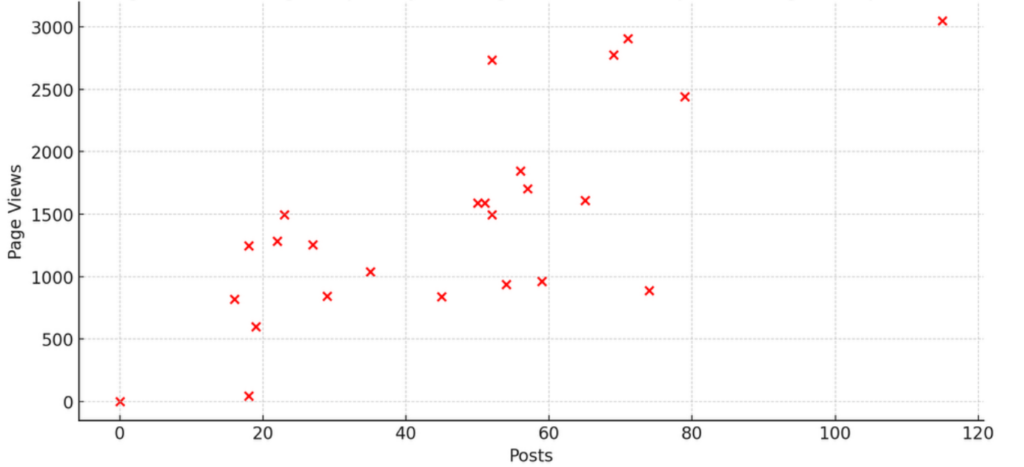
Figure 3 highlights the strong positive correlation between posting frequency and page views on corporate pages. This indicates a significant association where increased posting frequency leads to a substantial rise in page visibility.
References
Image 1. Taken from Make.com, created and copyright by Alderd J. Froolik designed automation scenario for Shopify catalog to LinkedIn.
Nguyen Tran Le Na & Nguyen Ngoc Hien | Len Tiu Wright (Reviewing editor) (2021) A study of user’s m-wallet usage behavior: The role of long-term orientation and perceived value, Cogent Business & Management, 8:1, DOI: 10.1080/23311975.2021.1899468
Robert C. Stern “LinkedIn Stats Looking Into 2023”. www.linkedin.com. Archived from the original on August 2, 2023. Retrieved September 17, 2023.
Roberto Mora Cortez, Wesley J. Johnston, Ayan Ghosh Dastidar, Managing the content of LinkedIn posts: Influence on B2B customer engagement and sales? Journal of Business Research, Volume 155, Part A, 2023, 113388, ISSN 0148-2963, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.113388.
Skivko M.O., Korneeva E.N. Digital Solidarity and the Use of Hashtags as a Way to Label the Ecological Communities. Communicology. 2023;11(1):131-141. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.21453/2311-3065-2023-11-1-131-141

